Quick Summary of the Article
Diabetes is a chronic condition that leads to elevated blood sugar levels, affecting the body’s ability to use glucose properly. This article highlights the various symptoms of diabetes and how to prevent it by adopting a healthy lifestyle and regularly monitoring blood sugar levels. It emphasizes the importance of healthy eating, physical activity, and stress management, along with basic diagnostic and treatment measures.
1. Introduction
- Diabetes is one of the most common chronic , affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs due to a defect in the production or use of insulin, leading to the accumulation of glucose in the blood. If uncontrolled, diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, and nerve damage. However, with awareness and good knowledge of the symptoms and prevention methods, the risks can be greatly reduced, improving the quality of life for those affected.
2. Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the pancreatic cells responsible for insulin production. It’s less common, mainly affecting children and young adults. Insulin is necessary for survival in this case, requiring regular injections to maintain blood sugar levels. - Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. Often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity, this type can be significantly controlled and even prevented through lifestyle improvements. - Gestational Diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs only during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. Although it usually resolves after childbirth, women who experience gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.

3. Symptoms of Diabetes
- Excessive Thirst
One of the early symptoms of diabetes is persistent thirst due to the body’s effort to eliminate excess sugar through urine, resulting in fluid loss. - Frequent Urination
As a result of drinking more water, the body needs to expel excess fluids, often leading to frequent urination, especially at night. - Fatigue
Despite eating, the body can’t use blood sugar for energy, leaving a person feeling tired all the time. - Unexplained Weight Loss
Even with increased hunger and food intake, diabetic individuals may experience rapid weight loss because the body starts using fat and muscle for energy. - Persistent Hunger
The inability to use sugar in the cells leads to constant hunger, even after meals. - Slow-Healing Wounds
High blood sugar levels can slow down wound healing by affecting circulation and weakening the immune system. - Skin Infections
Diabetics are more prone to skin infections, such as fungal and urinary tract infections, due to elevated blood sugar creating a favorable environment for bacteria and fungi to grow. - Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause fluid buildup in the lens of the eye, leading to blurry vision. - Tingling or Numbness in Extremities
Over time, high blood sugar can damage nerves, leading to a condition known as diabetic neuropathy, causing tingling or numbness in the hands or feet.

4. How to Prevent Diabetes
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for preventing type 2 diabetes. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can significantly reduce the risk. - Engage in Physical Activity
Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week, increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin. - Follow a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting added sugars and saturated fats can greatly reduce diabetes risk. - Avoid Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, so quitting or avoiding smoking is essential for overall health. - Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar, especially for those with a family history of diabetes, is key to early detection and prevention. - Manage Stress
Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels, so incorporating stress-management techniques like meditation or yoga is important for both mental and physical health. - Get Enough Sleep
Lack of sleep negatively affects blood sugar levels and increases the risk of diabetes. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. - Regular Check-Ups
Routine blood sugar checks are essential, particularly for individuals with risk factors such as a family history of diabetes or obesity. Early detection can help manage the condition before it worsens.
5. Diagnosis of Diabetes
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis of diabetes usually begins with a clinical examination, where the doctor assesses the patient’s medical history and current symptoms. Based on this information, the doctor may decide if additional tests are needed. Moreover, the clinical examination may include blood pressure measurement and body mass index (BMI) evaluation, providing a comprehensive picture of the patient’s overall health.
Blood Sugar Tests
When diabetes is suspected, doctors typically conduct tests to measure blood sugar levels. Several tests are commonly used in this context, including:
- Fasting Glucose Test: This test is done after the patient has fasted for at least 8 hours. A result of 126 mg/dL or higher may indicate diabetes.
- Random Glucose Test: This test can be performed at any time of the day, regardless of meal timing. If the result is 200 mg/dL or higher, it can be considered an indicator of diabetes.
- Hemoglobin A1C Test: This test provides an average measure of blood sugar levels over the past three months. A result of 6.5% or higher may suggest a diabetes diagnosis.
Additional Tests
In some cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests to confirm the diagnosis or assess potential complications. These may include evaluating kidney function, checking eye health, and conducting lipid tests.
Patient Follow-Up
Once diabetes is confirmed, regular follow-ups are essential. Routine check-ups help monitor blood sugar levels and ensure adherence to treatment plans. Additionally, medication or dietary adjustments may be required based on the patient’s needs.
Diabetes Education
It is crucial for patients to receive adequate education about diabetes, its symptoms, and how to manage it. Through education, patients can understand the importance of lifestyle changes and how to make healthy decisions. Education becomes an integral part of both the diagnosis and treatment process.
Psychological Support
Finally, diagnosing diabetes may require offering psychological support to patients, as this diagnosis can be overwhelming and impact mental health. A team of doctors and counselors can assist patients in adapting to these life changes and provide necessary emotional support.
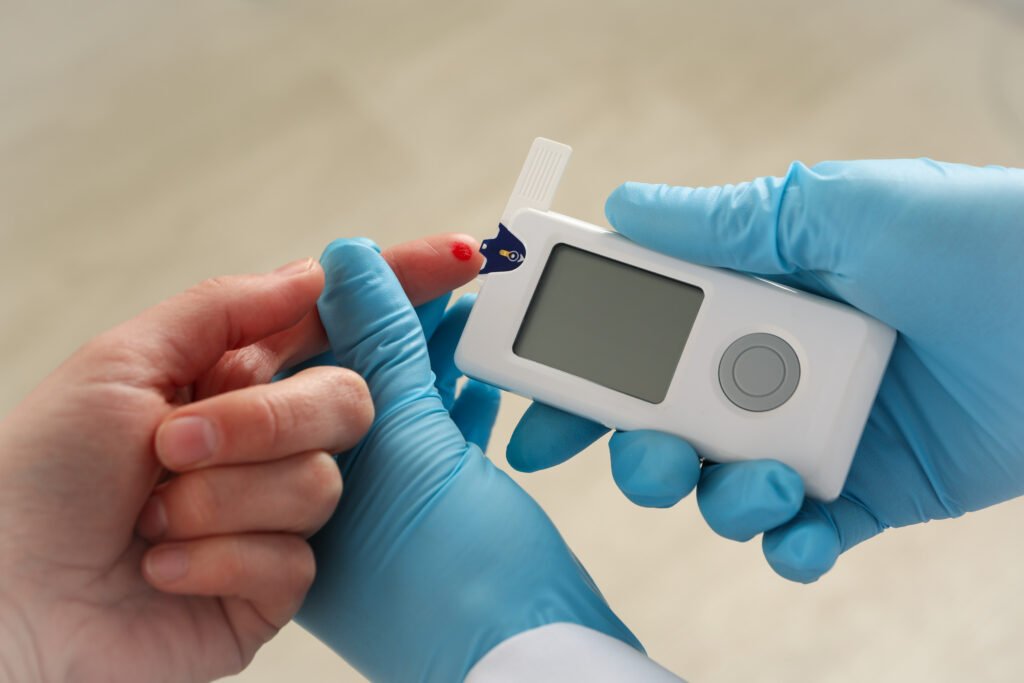
6. Managing Diabetes
Lifestyle Changes
Changing one’s lifestyle is a fundamental part of managing diabetes effectively. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding behaviors that may worsen the condition. When adhering to a healthy lifestyle, people with diabetes can reduce the need for medication and better control their blood sugar levels.
- Nutrition: People with diabetes should follow a diet with limited sugars and saturated fats, focusing on fiber-rich foods such as whole grains and vegetables. Eating smaller meals more frequently helps avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves the body’s insulin sensitivity and reduces blood sugar levels. Moderate activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are effective in managing diabetes.
Medication
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to control diabetes, necessitating the use of medications. There are several types of medications used to treat diabetes, ranging from insulin to oral drugs like metformin.
- Insulin: Primarily used to treat type 1 diabetes, it may also be used in advanced cases of type 2 diabetes. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels when the body cannot produce sufficient amounts.
- Oral Medications: Oral medications are commonly used in type 2 diabetes cases. These drugs work by reducing insulin resistance or enhancing insulin secretion from the pancreas.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications. Patients are advised to use at-home blood glucose meters for daily monitoring. This allows them to adjust their diet and physical activity based on the results and make better treatment decisions.
Psychological Support
Dealing with diabetes can be both a physical and psychological challenge, especially if it affects daily life. It is essential for patients to receive emotional support from family, friends, or diabetes support groups. In some cases, seeing a mental health specialist may be necessary to manage feelings of anxiety or depression associated with the disease. Strong emotional support helps patients adhere to treatment plans and manage the disease more effectively.

7. Conclusion: Promoting Health and Prevention
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires careful and ongoing management. However, individuals can minimize its negative impact on their lives by taking proactive steps to prevent or control it if already diagnosed. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes balanced eating, regular physical activity, and stress management helps improve quality of life and prevent complications. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and positive changes in daily habits can make a significant difference.

8. FAQs
What is the best diet for people with diabetes?
The ideal diet for people with diabetes includes limited amounts of sugars and saturated fats while focusing on fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Eating small, frequent meals helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Can diabetes be completely cured?
Currently, there is no complete cure for diabetes, but it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular blood sugar monitoring. Proper management prevents complications and improves quality of life.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 is caused by the body’s resistance to insulin or insufficient insulin production, often linked to factors like obesity and inactivity.
What exercises are recommended for people with diabetes?
Moderate exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming are effective in improving the body’s insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels. It is recommended to exercise for at least 30 minutes daily or as directed by a doctor.
How can diabetes be prevented if there is a family history of the disease?
Although a family history of diabetes increases the risk, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce that risk. This includes eating healthy foods, staying physically active, and maintaining a healthy weight.

